
The UX designer role occupies an exciting place in businesses today. In today’s marketplace, the customer is the KING! Every business needs to ensure that its customers are having the time of their lives with their products and services. The User-Experience domain is continuously climbing up on the ladder of priority of organizations. This has given the UX designer role a very prominent place in the industry. It has become one of the most sought-after jobs and has opened the gates of enormous scope for anybody who can shine in this niche. However, the definition of how a UX Designer should be like differs from company to company as each of them has different requirements and different customer bases. Nonetheless, the primary aim of a User Experience Designer is to ensure that the customer is not just satisfied but delighted with their services/products. They work towards improving the overall experience of the customer with the brand. It comprises of improvements like making the product more intriguing, engaging, and user-friendly. User-Experience designers think from the perspective of the customer to create the finest UX and solve any problems that a customer might face will indulging with the brand. Although the expectations from a UX Designer can vary from company to company, the general duties of the UX Designer include the following:
User Experience Designer Role:
Generally, the duties of a User Experience Designer includes the following:
1. Finding Innovative Ways To Solve Common UX Problems

A good UX designer is expected to think and move as a user would. He is responsible for figuring out the general issues that a user might face while using the product or indulging with an app. For instance, if the font is too small on your website or if the sign-up process of your mobile application is just too long and tedious. All these parameters come under the UX Designer role.
2. Product testing

A very crucial part of a UX designer’s job is to test various products to see how they are working with the users. A UX designer can conduct multiple surveys, interviews, usability tests, or take thorough feedback from the customers regarding their experience with the products/services and then gather the data and analyze it accordingly. The whole process of being with the users while they use your products creates a better sense of understanding and gives an in-depth knowledge of the customers’ experience with the product.
3. Conducting Comprehensive Product Research

This step is the most initial one while beginning a project. Detailed product research makes a firm ground for the designers to start building their projects and avoid assumptions and work with more factual data. This research enables designers to understand exactly what a user is looking for. It provides them with information about market requirements, customer expectations, and customer behaviour. It helps UX Designers to fathom industry models and perceive prospects for the product/service in a given region. It additionally boosts the planning and prioritizing of various parts of the products.
4. Describing Information Architecture

The primary task involved with Information Architecture is organizing the data and information athwart the product in a way that enhances the whole user experience. They ensure that the information is displayed across the product in a manner that is easily comprehended by the users. IA is the development of a framework for an application, site, or whatever that product/service that empowers users to know where they are on a site or an application, and data about the present location the user is. IA brings about the formation of routes, arrangements, and hierarchies.
5. Wireframing
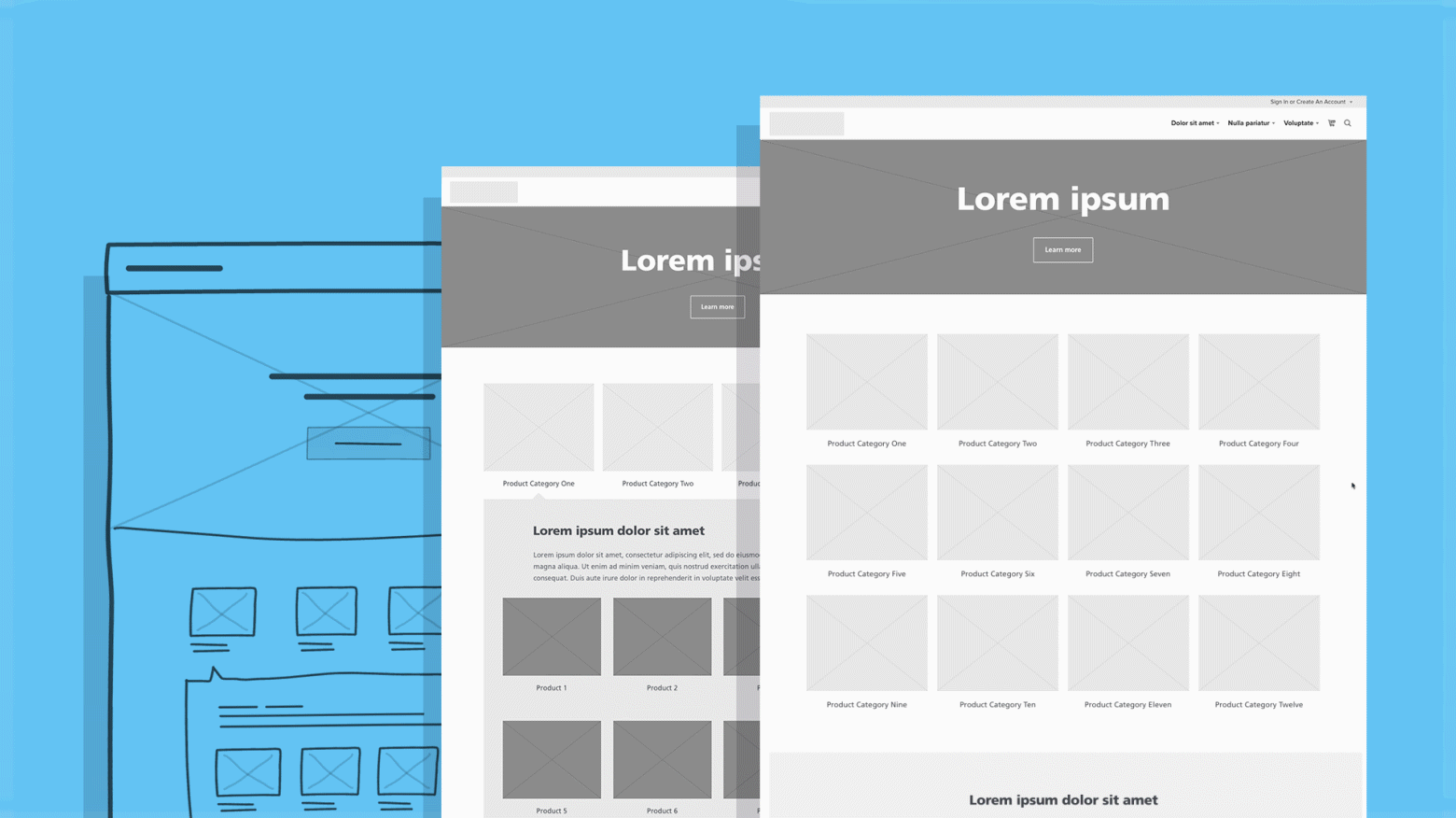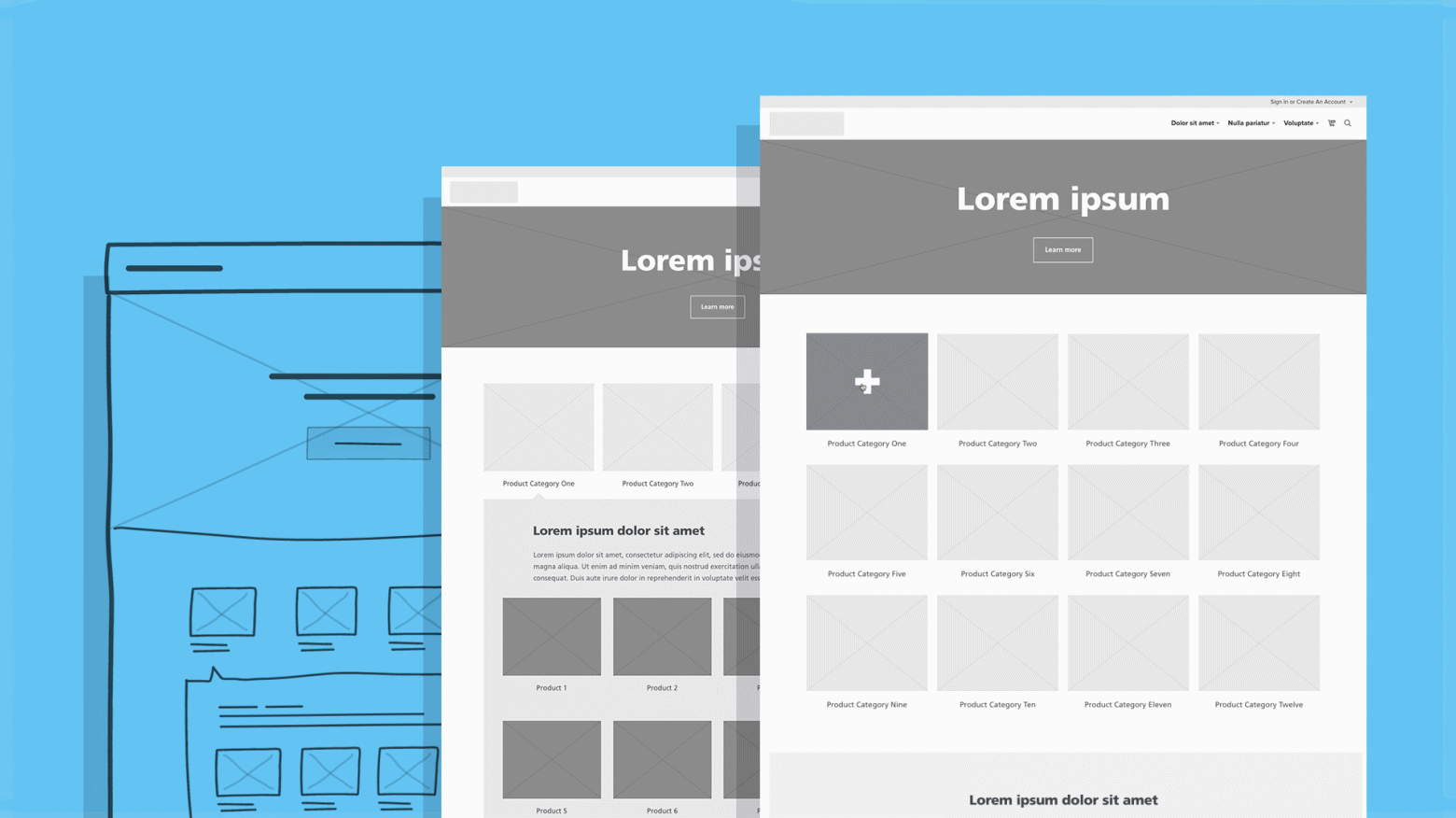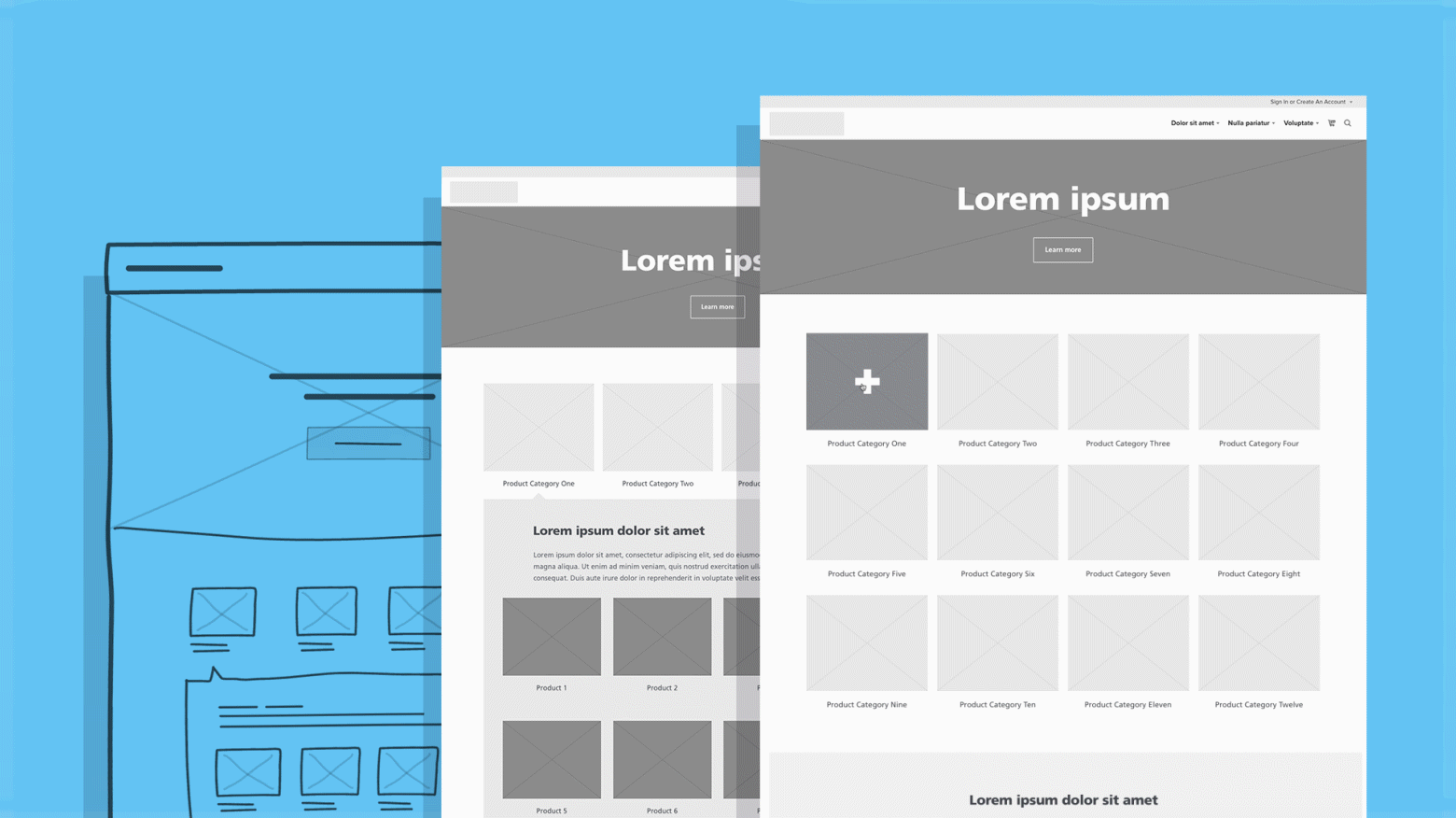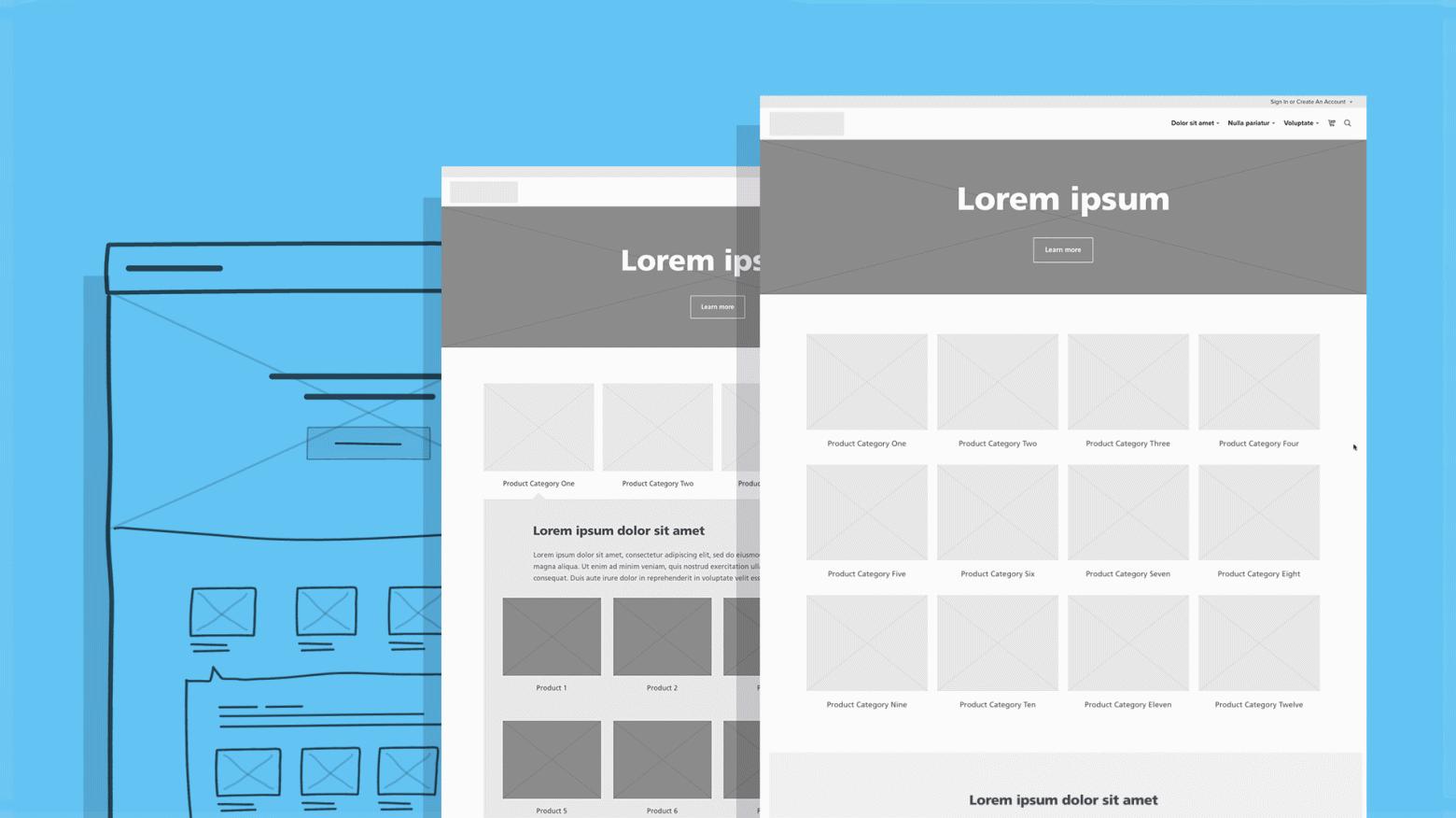
Wireframing is essentially a mock display of how the final product will look like. This strategy is very crucial to envision the product design and augmenting the entire UX. Wireframes depict each and every phase of the product and give comprehensive information about what a user might go through while interacting with the product. It provides an upper hand to the brand as it can figure out the drawbacks without actually presenting the product to the users. It saves time and maintains the brand’s reputation. However, wireframes are not used for actual product testing.
6. Designing

UX designers sketch the item’s plan dependent on the persona made toward the finish of exploring the target client. In this stage, the UX designer structures the substance per the situations/scenarios. Scenarios are narrative methods for speaking to the client’s excursion or a day in their life. They clarify how the item (regularly a site or application) fits into the client’s life. It is essential for a UX designer to precisely consider every phase of the client venture. In such a manner, UX designers regularly utilize the design practice of information architecture.
7. Testing

At this stage, UX designers find out about any issues that may emerge when clients connect with the product/services. Product testing might be as straightforward as observing clients or it might incorporate complex test strategies, for example, exhibiting differing renditions of the product to realize which performs the best. Designers may likewise conduct overviews and polls. Additionally, UX designers may talk with clients on the off chance that they recognize issue territories. The least difficult of all the client testing techniques is watching clients while they connect with the product/services.
8. Implementation

On the off chance that you’ve not had a lot of experience working with web developers, at that point, it’s critical to think about this pivotal part of the job. During implementation, you will be working personally with engineers to arrive at your ultimate objective for a venture. The engineers will be striving to change your thoughts and ideas into a genuine, working website; how you approach this relationship will decide the achievement or disappointment of your task. Keeping your engineers tuned in all through the procedure will make this last stage simpler for everybody included; you as the UX designer will have realistic expectations of what the developers can deliver (and in what time period) and the designers won’t get any terrible stuns ultimately.
A UX designer is answerable for this whole procedure, and its execution. In any case, bigger organizations will segregate this task into a couple of smaller jobs so that that attention is not divided.
Conclusion

UX Designing is a very vivid field as it does not just cover developing a product or selling it; it involves the through-out journey of a user with the brand. A different approach to the UX Designer role is to ensure that when a user uses the services/products, each component should be efficiently optimized and emerge as extremely easy-to-use and very practical. A company depends on its users, and ensuring that they have a pleasant experience is a serious business. Being a multidisciplinary field, UX Designing has an extensive scope. UX designers come from diverse backgrounds like psychology, engineering, designing, and even hospitality. To structure for human clients also implies that you need to work with an elevated degree of responsibility in regards to as inclusive as possible and consider the limitations and expectations of the masses. A User Experience (UX) Designer must have a solid comprehension of user conduct and business objectives and must be equipped for a wide assortment of aptitudes, going from psychology to structure and innovation. Even though UX designing is a field that feels essential to product improvement, its inherent capacity stays unidentified to numerous in light of its relative freshness.


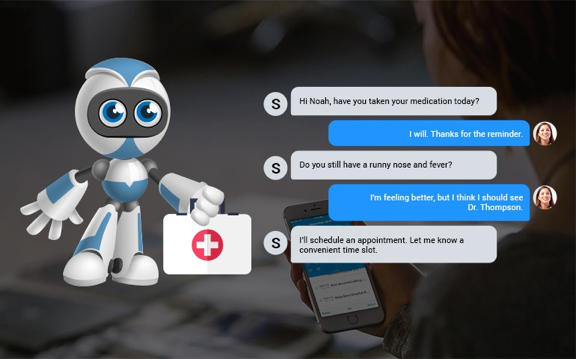
 The most challenging part for me was designing to handle the human-machine interaction. Each user is different. Unlike in websites/apps, where users can simply browse and leave, the chatbot users open the chat window to interact. They come with all sorts of questions- vague /smart /genuine /rogue /irrelevant and (sometimes) absurd. When they type a query, they expect the conversational UI to adapt to their needs–digest questions and construct intelligent answers/follow up questions.
The most challenging part for me was designing to handle the human-machine interaction. Each user is different. Unlike in websites/apps, where users can simply browse and leave, the chatbot users open the chat window to interact. They come with all sorts of questions- vague /smart /genuine /rogue /irrelevant and (sometimes) absurd. When they type a query, they expect the conversational UI to adapt to their needs–digest questions and construct intelligent answers/follow up questions.







/GettyImages-521983173-5ac9d827642dca0036e8c91a.jpg)



