What is malware?

Malware is short for ‘Malicious – Software”. The set of code or software that are made intentionally to harm and infect the endpoints in the network are known as malware. The cyber attackers use this malicious software to infect and attack the devices. The malware is of many types and is categorized based on the way they function. We will be explaining these later in the blog.
Malware Threats
These days, malware is not directly installed on the victim’s device. Instead, it is sent and installed on the endpoint device using some techniques and by exploiting loopholes. Thus, these are the scopes that are to be mitigated by the security professionals when deploying cybersecurity.
Various types of malware threats are:
- Social Engineering:
When an attacker manipulates the user to extract sensitive information for personal gains, it is known as social engineering. Sometimes the malicious links or malicious files are sent to the victim during social engineering. As soon as the victim clicks on the malicious link or downloads the malicious file, the malware gets installed in the victim’s device.
- Email:
The attacker sends lucrative emails that tempt the user to click on the link provided in the email. As soon as the link is clicked, the malware gets downloaded itself in the background and infects the user’s PC.
- Website cookies:
Malware tampers web cookies. Thus, when you open a genuine site, this malicious cookie triggers and redirects you to the malicious sites. Thus, these sites may extract information or can download the malware into your system.
- Planted Removable Medias:
Sometimes the attacker intentionally plants the removable media with malware loaded in it to tempt the victim to check its data. As soon as you will plug it in your system, the malware will be automatically installed and will end up infecting your device.
Types of malware
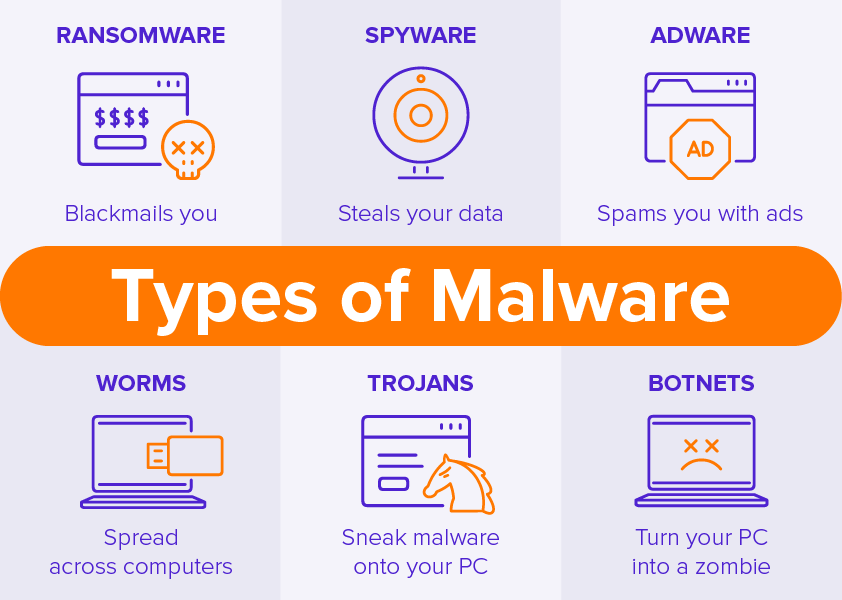
As told earlier in the blog, the malware is categorized and named based on the way they infect the system. Some of them are as follows:
- Worm:
Worms exploit your operating system. These types of malicious software use your network bandwidth, steal your data, and send it to the attacker. It has the property to self-replicate and thus, it copies itself through the network.
- Trojan Horse:
Trojan Horse is that comes attached to a normal file. Trojan malware disguises itself in the necessary files and then sends the data of your device to the attacker.
- Spyware:
This extracts important credentials of data from a user’s device and sends it to the attacker. This kind of malware exploits the vulnerabilities in the software.
This is a kind of malicious software that infects the victim’s device by encrypting its data. The data can only be decrypted with a key that is provided by the attackers once you pay the ransom amount to them. Thus, it is advisable to keep backup of your data.
- Adware:
Adware is a kind of malicious software that is injected into the victim’s device using the advertisement pop-ups of needful software. Pop-ups of urgent requirements of antivirus, malware remover, etc. are embedded with the malicious link. As soon as the victim clicks on the link, the malicious file is downloaded in his/her system and infects the device.
- Virus:
This is a kind of malicious software that steals information and credentials of the user. The virus is also sometimes used to make the victim a bot. It can self-replicate itself but it cannot be transferred to the other device without human intervention. It can be attached to a document, mail attachments, scripts, etc.
6 Prevention tips from malware

- Never click on not so secure and lucrative links as they may end up infecting your system.
- Always keep your PC’s operating system updated.
- Do not click on any link unless provided by the trusted source.
- Change your passwords in the necessary interim intervals.
- Avoid opening emails and attachments from unknown resources.
- Do not pick up USBs found lying unguarded in public spaces.
- Be cyber aware.


