The backend is the part of a web application that is unrevealed to the user. Unlike front-end, back-end development operations are not very easy and usually turn out to be complicated and manifold; this part is in alignment with the server. Backend operations are a lot different that are controlled by different programming languages like C, C++, Perl, and Ruby. It is a broad field that’s further subcategorized into several levels.
A backend developer usually doesn’t work alone; backend developers usually work in teams of 2 or more people. A team of backend developers contains different specialists that are responsible for their specific discipline. Some are responsible for database management, some work with caching schemes and scripting while some focus on website architecture. Behind every successful website and application, the combined effort of the whole team plays its role. A backend developer’s code bridges the communication between database and browser.
To describe the working of a backend developer in a nutshell, we can say that such a developer mainly focuses on the following:
- Web Development Languages
- Database and Cache
- Server
- API (REST & SOAP)
The essential requirement for becoming a backend developer is to have a keen knowledge of at least one server-side programming language.
What is the role of a backend developer?
To understand the skills required to become a backend developer, one needs to analyze what are their responsibilities. Only then we can relate their skills to their roles and responsibilities. The key responsibilities of backend developers are:
- They work with front-end developers and provide server-side algorithms of user-facing web application elements. Backend developers code in server-side language to create logic so that web applications function correctly.
- Other than coding and creating functional web applications, backend developers also optimize them for increasing response time and efficiency.
- They analyze the goals and requirements, handle bugs and errors, and come up with solutions.
- They also interact with the database for storing data and ensure that every user has access to what they search.
- They also manage APIs that are executed across the devices.
- They are also involved in building the architecture of the system.
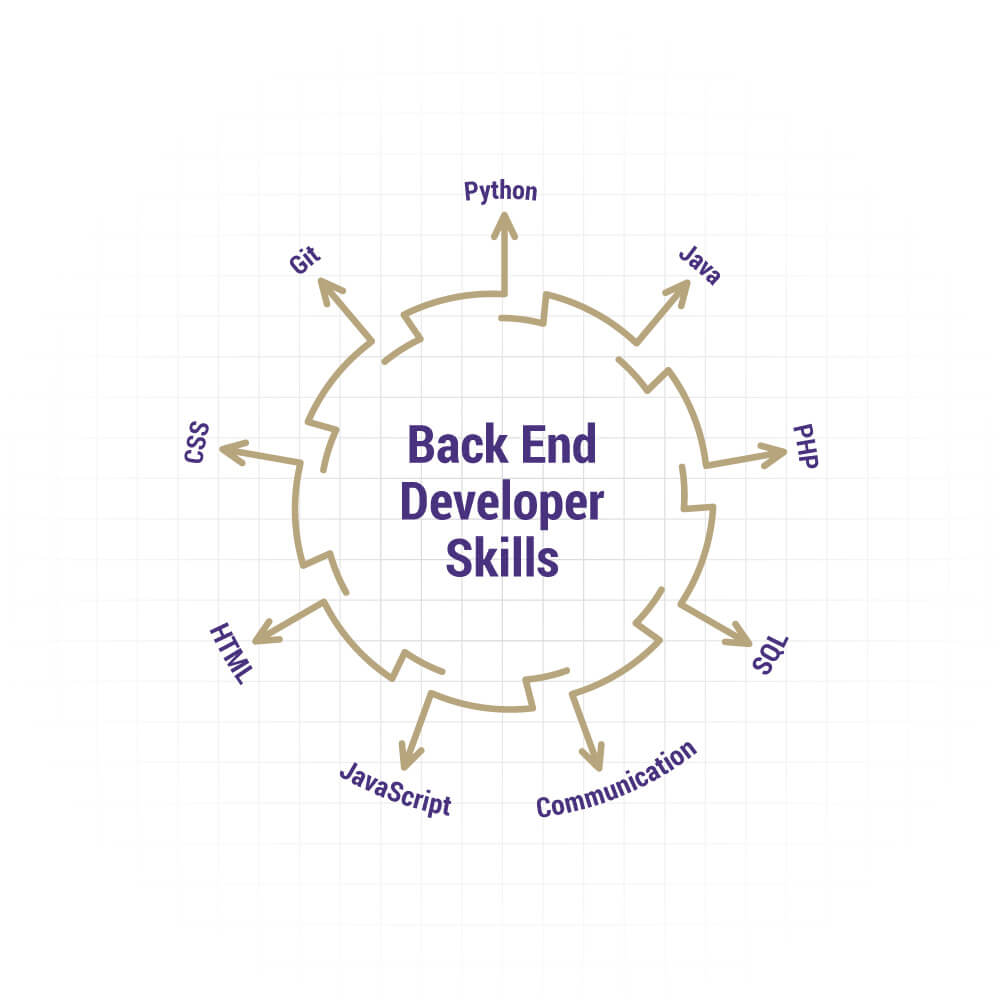
Backend Developer Skills

To have efficient backend developer skills, one needs to have complete command on the subject. A good developer is aware of every new trend and invention in his domain. He urges to learn and align with all advancements coming his way.
Technology progresses every day. Many innovations are being made, and adapting to modern techniques is imperative to sustaining the game. Luckily in the development domain, a new trend might be complicated in learning, but it is focused on reducing the coding effort. Every new language aims to have minimal syntax, and it is suitable for a developer to invest some time to learn it.
The necessary technical skills required to become a backend developer are:
- In-depth knowledge of at least one backend programming language and framework.
- Knowledge of front-end technologies, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, so that he can communicate with the front-end team.
- He should be capable of managing a hosting environment along with the database administration.
- He should be capable of scaling applications to handle the load changes.
- He should have enough knowledge of accessibility and security compliance.
- It’s good for him to have an experience of version control, such as GIT.
- A backend developer is not expected to have command on every programming language. That is not possible for a human to have expertise in each of them. But they are expected to be experts in their opted language.
More Backend Developer Skills to add on the resume
1. Web Development Languages: Back-end developers work simultaneously with front-end developers, setting server rationale to outside components of the web application. So as to execute this rationale, the backend engineer utilizes server-side scripting language. The best programming languages that you must know while talking about backend developer skills are:
- Ruby: Ruby is a programming language that is utilized accompanied by Rails. Ruby is to Rails as PHP is to Zend, or as Python is to Django. The sheer class and finesse of the language are what attract the back-end developers towards this language and make it a must-have in your tech stack. It prioritizes conventions rather than configuration, which helps the back-end developers as they don’t have to waste their precious development time in configuring the files to start the development process.
- Python: Curated by Guido van Rossum and rolled-out in 1991, Python is an interpreted, cutting-edge, general-purpose programming language. It reduces the need of coding to a very significant level and has high utility because of the presence of third-party modules. The ease of use and extensive libraries offer back-end developers more productivity as compared to other programming languages. Not just for building basic applications like desktop apps, Oss, Business Apps, and web frameworks, but Python is also the best fit for AI and ML-based web development.
- PHP: PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is an open-source back-end scripting language used by developers to build web apps and sites. PHP also has a huge assortment of utilitarian modules and a couple of the modules accessible in PHP incorporate Graphics and PDF, among others. One of the greatest advantages of PHP is that it is very easy to learn and use because of its simple syntax. Anyone who is familiar with C language can easily grasp PHP without any difficulty.
- Java: Java is an object-oriented, platform-independent, general-purpose programming language that is designed to have negligible implementation reliance. As a result of Java’s power, convenience, cross-stage capacities, and security highlights, it has become the most preferred language among developers.
2. Comprehensive Knowledge of Databases: Become familiar at stacking and recovering data from databases. Though front end developers can associate with databases and interface with them too, server-side development is right now the standard method to control advantaged and extraordinary access to that information, including storage and recovery. Start with great social style databases, and move towards chart databases as your knowledge permits.
3. Connecting to Application Programme Interface (API): Internet browsers aren’t the only entity to interact with web applications. Regularly, an organization will offer a mobile app for iOS or Android alongside its principal site. There are additionally program based applications that principally utilize JavaScript, not server-side rendered HTML (through structures like React, Vue, or Angular). To recover information for the display, these applications require an Application Programmer Interface, or API to associate with.
HTML might be helpful for designing substance in internet browsers, however, there are greatly improved configurations for information that will be utilized by different projects. The two most mainstream positions for API information are JSON, which represents JavaScript Object Notation, and XML, which represents eXtensible Markup Language.
4. Server Handling: Your site needs a database to deal with all the client and product data. A database stores site content in a structure that makes it simple to recover, arrange, alter, and store information. It runs on a remote PC called a server. There is a wide range of databases that are generally utilized, for example, MySQL, Oracle, Postgres SQL, and SQL Server. For server management you can choose any one of these and acquire an expertise on it: Docker, Kubernetes, Nginx, Node.js, New Relic etc.
5. Knowledge of Popular Frameworks: You must have knowledge of the frameworks identified with your preferred language. For example, on the off chance that you go with Java, you would be required to know Spring, Hibernate, and so on. These are well known Java-based frameworks. Additionally, on the off chance that you go for Python, you would be required to know Flask, Django or some other Python-based framework.
Estimated income of a Backend Developer
According to research, and taking the previous year’s figures into consideration, backend developer trends to earn up to $120,798 per year. This figure could vary based on expertise, experience, skills, and is also dependent on the company, country, and other factors. Also, it is worthwhile to note that there’s a vast difference between the pay-scales of backend developers and front-end developers. Front-end developers aren’t paid as much as backend developers. The reason is that front-end work is mostly done with the help of automated tools, while backend development requires much technical expertise.
What is the future of Backend Development?

As of the current market trends, there are no worthy alternatives to backend developers and backend development. So naturally, the future is very bright for such developers. In this digital age, every business is required to have an online presence, and for that, they require high-quality backend development for their websites. Although many clients are not aware of the difference between backend and front-end still, the market cannot survive without backend developers. Despite technology replacing everything with automation, backend developers have a safe future as they are required for the process of developing automated tools.
Summary
The role of backend developers is critical to web development. They are responsible for all the key roles and ensure the deployment of quality products. That is why more and more aspiring web developers are today opting for this career. Such people should have a passion for coding and possess all the required knowledge and skills to become an efficient developer. It is also necessary to have other additional skills, mentioned above, to make your mark in the market.