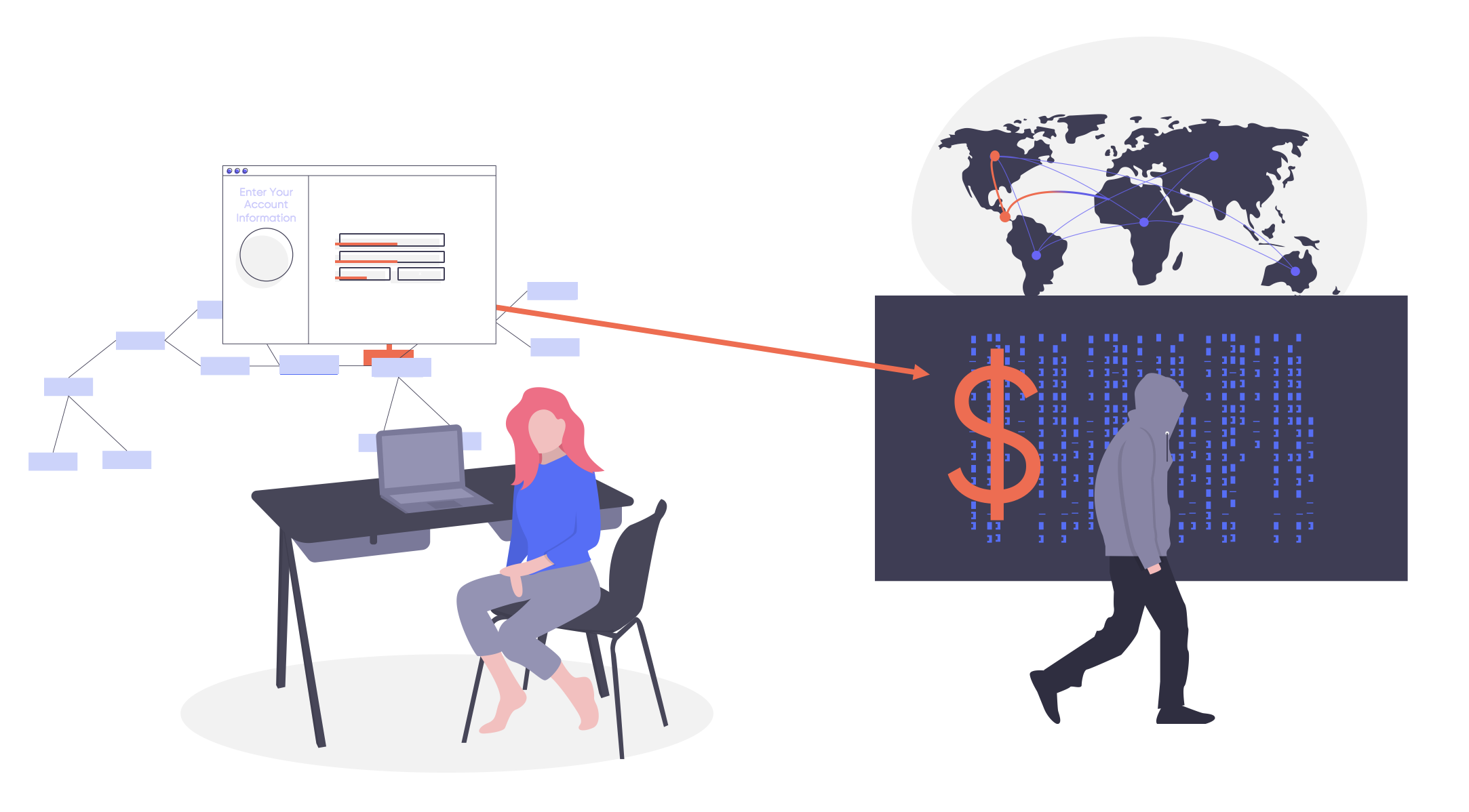
E-skimming has been an online shopping threat for a long time, keeping pace with the growth of e-commerce overall. The current global crisis presents another big opportunity for hackers to launch these strikes as people increasingly shop online. The nefarious cybercrime targets online payment systems to collect or “skim” the payment details of customers’ payment cards at the checkout.

Unlike more traditional cyber attacks, where an entire customer database may be targeted in a single hit-and-run attack, skimming attacks continually intercept customer payment details at the point of purchase, making them harder to detect and often invisible to both customers and retailers.
Several criminal groups have become very adept at this kind of attack over the years, the most prevalent and successful of which is known as Magecart. Magecart is an umbrella term for a set of sophisticated criminal groups using similar malware and techniques — all with the goal of stealing credit card information from online retailers.
The Magecart groups are known to have been active since 2016 and have been behind some of the largest payment system attacks in recent years, including British Airways (2018), Newegg electronics (2018), the Atlanta Hawks Shop fan merchandise store (2019), Forbes magazine subscriptions (2019), as well as ticket-reselling websites for the 2020 Olympic Games and the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) Euro 2020 soccer tournament (2020). Such attacks earned Magecart a position on Wired magazine’s “Most Dangerous People on the Internet” list in 2018.
How it works
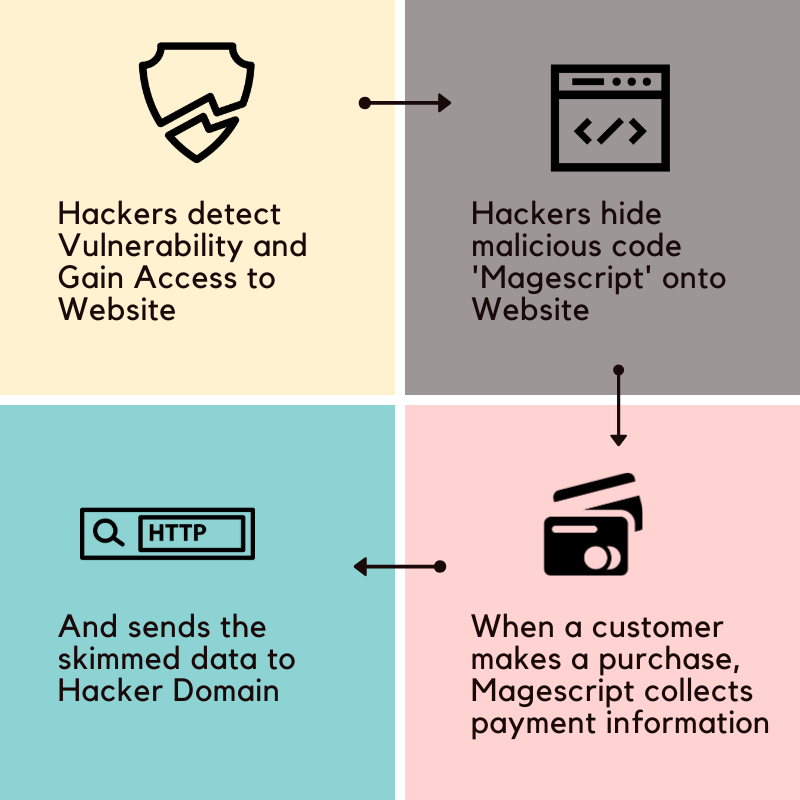
In most skimming attacks the threat actor introduces some additional code to a retailer’s e-commerce application. Recent attacks by the Magecart group have achieved this through the compromise of a trusted external third party whose code is legitimately included in the application, such as an external code repository, a chatbot or an advertising vendor.
So far, researchers have identified more than 40 different code-injection exploits, sometimes as small as 20 characters, which can be difficult to detect unless the application code is examined line-by-line for changes.
Attackers have also incorporated the use of valid SSL certificates tied to the domains that deliver malicious code, making traffic appear legitimate and preventing customers from receiving mixed content warnings when the website attempts to mix trusted, encrypted website content with malicious content that is served unencrypted.
A recent report has also described Magecart attacks where misconfigured access controls on Amazon S3 buckets allowed the attackers to tack their skimmer code onto existing JavaScript application code files.
Defending against card skimming

The best proactive cyber defense an organization can implement to defend against card-skimming attacks all focus on hardening the e-commerce application stack and limiting what code is allowed to run.
- Use a free online scanning resource to help spot suspicious connections being opened by scripts injected into the application. Browser developer tools can also be used to analyze contents and spot suspicious connections made during a customer session.
- Use the Amazon “Block Public Access” option on any S3 buckets in use by the organization to prevent unauthorized changes to application files.
- Define a Content Security Policy (CSP) that defines a list of locations that resources can be loaded from on your site. This should be applied to all sensitive pages, such as payment pages, login pages and other areas where users may enter sensitive information.
- Verify any external scripts, such as those from advertising partners, using Subresource Integrity (SRI). This will ensure that any scripts included from external sources are hashed and checked against a known good value to ensure that they are the files that you expect to be loaded and if not, they are blocked from loading by the browser.
- Make sure that all assets on sensitive pages use SRI. Using the “require-sri-for” directive in the CSP to enforce SRI on all scripts and style tags will prevent assets being included on these pages that do not have SRI enabled.
The activity seen from Magecart and similar adversaries demonstrates that these are a persistent and resilient threat. The lucrative nature of card-skimming attacks ensures that attacks will continue to evolve in both stealth and capability in response to security precautions. However, for many of the attacks we have seen from these groups to date, had the measures described above been implemented, they would have gone a long way toward preventing some very embarrassing and expensive breaches.